 Signatures have been used to authenticate documents for a long time. Only you can sign and anyone can make out that the signature belongs to you. This is very similar to public and secret keys, where secret key is analogous to signing and the public key to verifying the signature.
Signatures have been used to authenticate documents for a long time. Only you can sign and anyone can make out that the signature belongs to you. This is very similar to public and secret keys, where secret key is analogous to signing and the public key to verifying the signature.
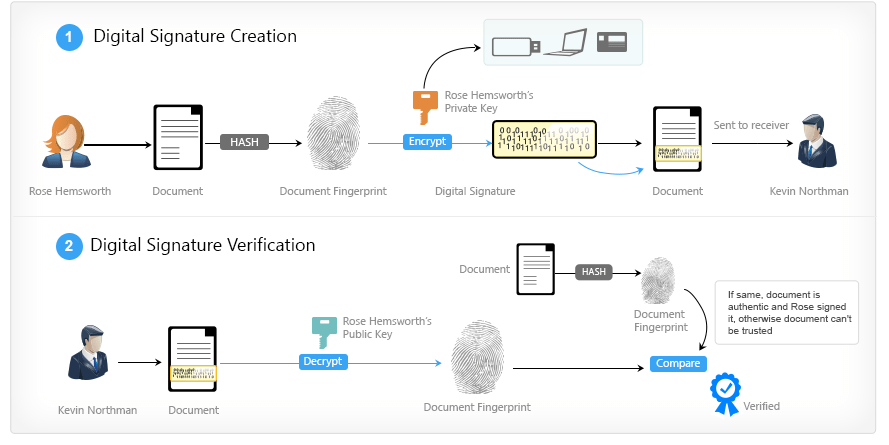
How do you ensure that the contents of the document have not been tampered with after you have signed the document?
One way is to encrypt the entire document but this will take along time to decrypt. A convenient way is to encrypt a message digest, which is generated by applying a mathematical function on the document. Even one character change in the message will result in the message changing in an unpredictable manner. The message digest is much smaller than the document and takes much less time to encrypt and decrypt. The encrypted message digest is called ‘digital signature’. It is sent alongside the message that is not encrypted.
At the receiving end, first the ‘digital signature’ is decrypted using the public-key to obtain the message digest. Subsequently, using the same mathematical function on the document, a message digest is generated and the two message digests are compared to be identical. If there is a difference, then either the document has been tampered with or it is not signed by the authorized person.
The mechanism discussed so far can ensure privacy, authenticity of source, repudiation by the source and integrity of data communication. The only weak link in the chain is the veracity of the public key. Digital certificates take care of that.
Sponsored Link: Contact us for Free web Design Demo